| |
The Finest Pest Control Company in NorthEast, Ohio
Pest Control • Animal Trapping • Chimney Caps/
Exclusions • Termite
Treatments
Pest Identification
Please Select Your Pest: |
 |
|
|
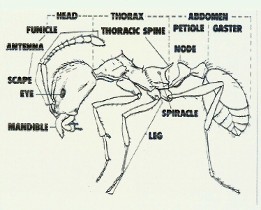
(Hymenoptera) |
Characteristics: - Social insects
- Different species identified by number of nodes
- Different species have different sizes of workers
- A colony consists of
- 1 or more reproductives
- Collection of workers
- Eggs, larvae, and pupae
- They may nest in the ground, wood, cement, and wall voids
|
|
|
 |
Bees, Wasp, Hornets, and
Yellowjackets |
|
(Hymenoptera) |
Description: - Some are social and live in colonies (Vespidae)
- (nests)Queen, Eggs, Workers, and brood
- Paper wasps, Hornets, and Yellowjackets
- Some are solitary (Sphecidae)
- No colonies
- an adult female builds a nest for each egg and leaves an insect
for the larvae to eat.
- Mud daubers and digger wasps
|
|
|
 |
|
|
(Isoptera) |
This includes - Termites
- Powderpost Beatles
- Carpenter ants
- Carpenter Bees
|
|
|
 |
|
|
(Dictyoptera) |
Characteristics: - They produce odorous secretions from various points in their
body which can affect flavor of foods
- They have disease producing organisms on their bodies
such as bacteria, protozoa, and other microorganisms
- Different forms of gastroenteritis is transmitted
- Food poisoning, nausea, abdominal cramps, vomiting, diarrea,
dysentery, and other illnesses
- Their excrement and cast skins can contain allergens that can
cause allergic responses in humans such as
- skin rashes, watery eyes, and sneezing
History: - Most common insects
- Known to be present on Earth for 350 million years
- Sizes vary considerably
- One of the most adaptable insect group
- Approximately 3,500 species worldwide
- 70 species in the US
- German cockroaches are most prevelant species encountered in
the US
|
|
|
 |
|
|
(Coleoptera) |
Characteristics: - Identified by their feeding habits
Feeding habits of Stored product
pests: - Internal feeders
- Feed within kernals of whole grain
- External feeders
- Scavengers
- Feed on grain only (after seed has been broken)
- Secondary Pests
- Feed on matter that is in the deteriorting phase
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
Description: - Pests that occur in buildings
- They do not complete life cycle in buildings
|
|
|
 |
Flies and Mosquitoes |
|
(Diptera) |
Description: - Fourth largest order of insects
- Food source to many animals and some plants
- Help recycle nutrients of manure back into the ground
- Can cause disease in humans and animals
- Breed in and feed on decaying organic matter
|
|
|
 |
Fleas, Ticks and other
Ectoparasites |
|
(Ectoparasites) |
Description: - Arthropods that lives on or feeds from its host for entire life
cycle
- Parasites that feed on the external surface of the host
- They feed on
- Some carry disease causing organisms such as
- bacteria, protozoans, rickettsias or viruses
|
|
|
 |
|
|
(Muridae and Cricetidae) |
Description: - Part of the mammalia class
- They are commensal and semi commensal rodents
- Live in all types of habitats on Earth
- Cryptobiotic:
- Kinesthetic:
- Can memorize muscular movements to travel a path
- Olfaction:
- Causes serious health issues among humans
|
|
|
 |
|
|
(Animal) |
Any wild vertebrates, other than commensal rodents and birds |
|
|
 |
|
|
(Aves) |
Description: Birds as pests - Cause agricultural damage
- Can damage aircraft and structures
- Can cause disease that affect humans and animals such as
- histoplasmosis, chlamydiosis, and salmonellosis
- A variety of ectoparasites (mites, ticks)
- Can bite humans
- Can bring arthropods into nesting sites
- Can cause noise
- Can displace other preferred species
- Can ruin areas with their droppings
|
|
|
|
|
|







